
Madison Farmer’s Market Scenes June 3, 2011



Trout….

The Dilemma
If there is one most frightening thing that war always exposes, even if one is on the winning side, it’s weakness in the supply logistics. While most never consider it, official policy often changes during a war because supplies that are critical to the war effort seem in danger of being disrupted. Such jeopardy, moreover, forces the accountants, economists and politicians waging the conflict to start thinking about how the world will be changed once the fighting has ended.
Few today appreciate the fact that our foreign policy, particularly as it is tied to the Middle East, came about because of just such concerns in the first years of the Second World War. As one might expect, that official policy was based on real fears that America would one day run out of oil.
“The European War”
It was the summer of 1941 and the State Department had requested that the White House include Saudi Arabia in our Lend Lease program. It wasn’t because the Saudis were going to become a direct ally against the European Axis Powers, but because we were about to embargo U.S. oil shipments to Japan. Many believed – correctly, as it turned out – that this would probably lead to hostilities with Japan that would draw us into the war.
Standard Oil of California, which had been drilling for oil in Bahrain for over a decade, now had oil concessions granted by King ibn Saudi. The first six wells Standard drilled into the Arabian desert were nothing to write home about, but when Well No. 7 came in on March 4, 1938, the engineers and wildcatters all knew that Saudi Arabia was going to be an oil bonanza.
Yet on July 18, 1941, Roosevelt refused the request for Lend Lease for Saudi Arabia. He saw no immediate benefit to diverting U.S. dollars overseas simply because Standard had oil concessions there. In any case, the outbreak of the European War in 1939 had reduced oil production in the Kingdom to an insignificant volume — a trickle, considering that American oil amounted to 60 percent of the world’s crude at the time. Instead Roosevelt asked Federal Loan Administrator Jesse Jones to look into the possibility of having England deal with the Saudi King’s pressing needs.
Stupid IT Tricks: Medical Records, or Why a Federal Subsidy Makes No Sense (I Agree)
A reader asked me to write tonight about the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act, which is about as far from something I would like to write about as I can imagine, but this is a full service blog so what the heck. The idea behind the law is laudable — standardized and accessible electronic health records to allow any doctor to know what they need to know in order to treat you. There’s even money to pay for it — $30 billion from the 2009 economic stimulus that you’d think would have been spent back in 2009, right? Silly us. Now here’s the problem: we’re going to go through that $30 billion and end up with nothing useful. There has to be a better way. And I’m going to tell you what it is.
But first a word from my reader:
A Few Memorial Day Weekend Photos @ the Madison Arboretum
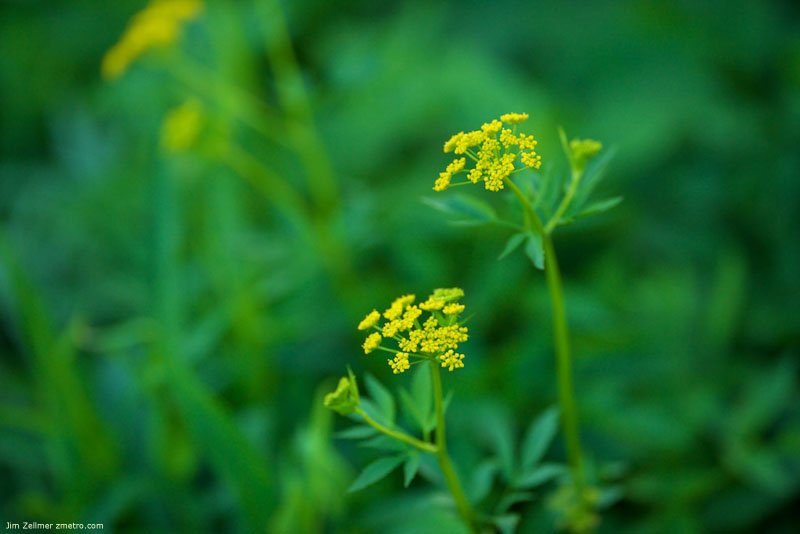
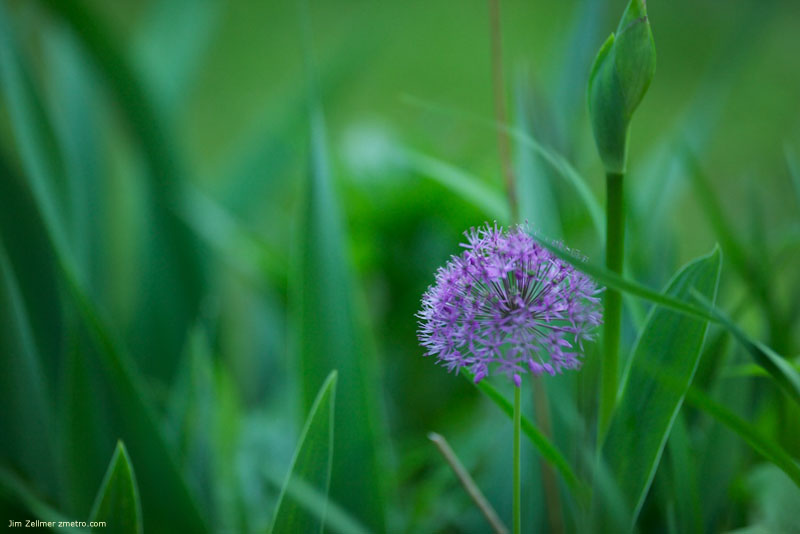
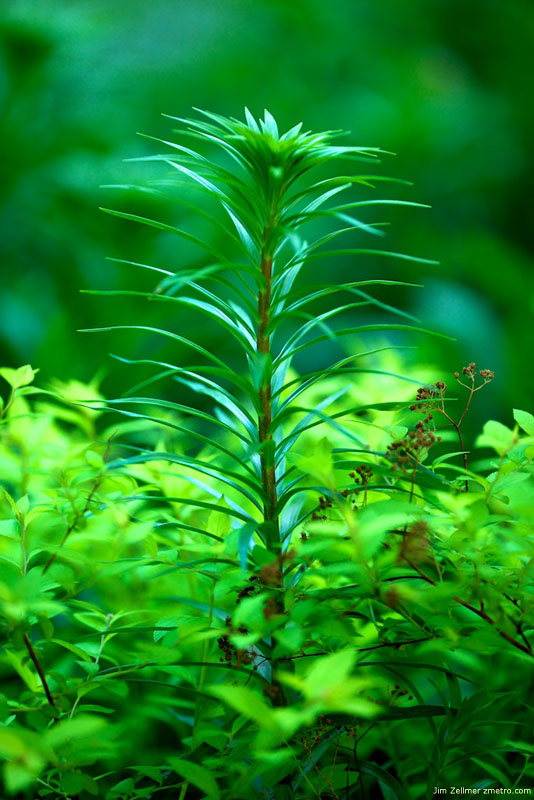
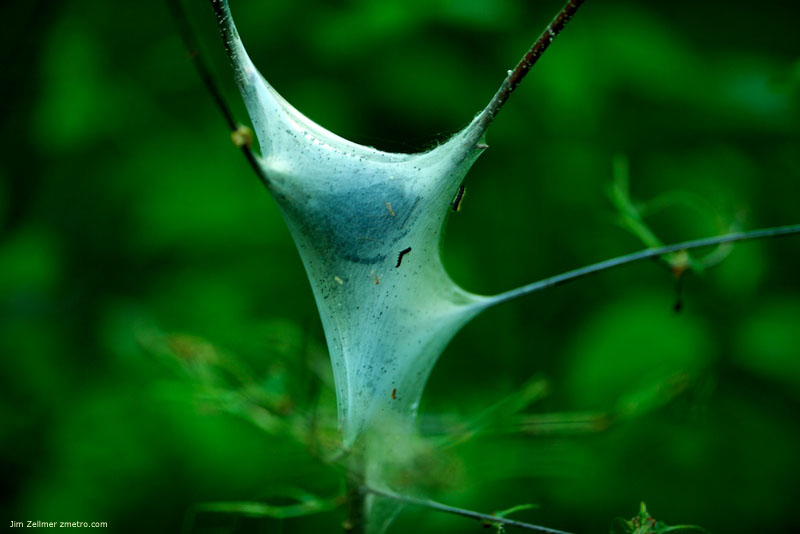








The places in between
There are those who believe that technology has hijacked the whole of the visitable earth, snatched it away, miniaturised and simplified it, making travel so accessible on a flickering computer screen that there is no need to go anywhere except to your room. In a related way, the travel book is believed to have been not just diminished but made irrelevant by the same technology. Since we know everything – the information is easily dialled up – and the world has been so thoroughly winnowed by travellers, what is the use of a travel book? Where on earth would you go to remark each anxious toil, each eager strife, or watch the busy scenes of crowded life? Surely it has all been written.
This isn’t a new conjecture. In 1972, in a blasé magazine piece of postmodernism, entitled “Project for a Trip to China”, the American writer Susan Sontag sat in her New York apartment ruminating on China. Sontag was that singular pedant, a theorist of travel rather than a traveller. She concluded her piece: “Perhaps I will write the book about my trip to China before I go.”
To such complacent and lazy minds, here is a suggestion. Try Mecca. After prudently having himself circumcised, learning to speak fluent Arabic, dressing as an Afghan dervish and calling himself Mirza Abdullah, the British explorer Sir Richard Burton travelled to the holy city of Mecca, a deeply curious unbeliever among devout pilgrims. This was in 1853. He published his account of this trip in three volumes several years later, his Personal Narrative of a Pilgrimage to Al-Madinah and Meccah. The last non-Muslim to do this and to write about it was Arthur John Wavell, of the distinguished British military family. An army veteran, and farmer in Mombasa, Kenya, Wavell developed an interest in Islam. In order to know more, he disguised himself as a Swahili-speaking Zanzibari, made the pilgrimage and wrote about it in A Modern Pilgrim in Mecca (1912). Wavell took the trip in the winter of 1908-1909, more than a century ago. No unbeliever has done it since. Now there’s a challenge for a technology-smug couch potato who prates that the travel book is over. Of course, this daring trip is not easy. It is, perhaps, not a journey for a gap-year student wishing to make his or her mark as a travel writer but it is a book I would want to read.
Studying Housing Through Distorted Indexes
There is some reason, however, to think that the recent price declines may be overstated by the index. The figures are based on sales of the same home over time, but there is no way to measure changes in the quality of a home.
With many homes now being sold in distress, either because of foreclosure or as “short sales” in which the sales price is below the amount owed and all the proceeds go to the lender, it is likely that some of the homes were in poor condition. In addition, such sales are often made for lower prices than comparable homes could obtain if sold without time pressures. If and when nondistress sales become a larger part of the market, that could cause the index to rise even if the overall market is not getting stronger.
Lessons from war’s factory floor
The lowest point of the US occupation of Iraq was about five years ago. American forces had no effective strategy in the face of a street-level civil war and a particularly vicious insurgent group, al-Qaeda in Iraq. At Haditha, frightened and frustrated marines had killed 24 civilians. At Samarra, the Golden Dome mosque had been destroyed – a potent symbol of conflict between Shia and Sunni Muslims. Donald Rumsfeld, then defence secretary, appeared to be in an advanced state of denial, breezily waving away good advice, and in a notorious press conference shortly after the atrocity at Haditha, refusing to use the word “insurgent”, or to let the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff use it either. The US strategy was failing and its leadership was determined not to change direction. It was a case study in organisational dysfunction.
Yet by 2008, the situation in Iraq had improved radically. Al-Qaeda in Iraq was in retreat, and the number of attacks, American and Iraqi deaths had fallen dramatically. Although the success remains fragile and there were other factors involved, a complete transformation of US military strategy deserves much credit.
How did it happen and what are the lessons for other organisations that need to turn around? The easy answer is that the solution was a change of leadership. Thanks to behind-the-scenes campaigning and a drubbing in the midterm elections for President George W.?Bush, Mr Rumsfeld was replaced, and General David Petraeus was put in charge of the war in Iraq.
Henry Kissinger talks to Simon Schama
Not so much, though, as to get in the way of treating China as an indispensable element in any stabilisation of perilous situations in Korea and Afghanistan. Without China’s active participation, any attempts to immunise Afghanistan against terrorism would be futile. This may be a tall order, since the Russians and the Chinese are getting a “free ride” on US engagement, which contains the jihadism which in central Asia and Xinjiang threatens their own security. So was it, in retrospect, a good idea for Barack Obama to have announced that this coming July will see the beginning of a military drawdown? The question triggers a Vietnam flashback. “I know from personal experience that once you start a drawdown, the road from there is inexorable. I never found an answer when Le Duc Tho was taunting me in the negotiations that if you could not handle Vietnam with half-a-million people, what makes you think you can end it with progressively fewer? We found ourselves in a position where to maintain … a free choice for the population in South Vietnam … we had to keep withdrawing troops, thereby reducing the incentive for the very negotiations in which I was engaged. We will find the same challenge in Afghanistan. I wrote a memorandum to Nixon which said that in the beginning of the withdrawal it will be like salted peanuts; the more you eat, the more you want.”